Software Engineering and Design
Home | Code Review | Databases | Software Engineering & Design | Data Structures & Algorithms
Narrative
The artifact I chose is a combination of final projects from CS 250: Software Development Lifecycle, IT 315: Object Oriented Analysis and Design, and CS 320: Software Testing, Automation, and Quality. The code part is directly from CS 320: Software Testing, Automation, and Quality. It was created October 2019. This artifact showcased the different testing methods done on a code for a medical application in Java. As for the other two final projects, I will take aspects of them and show the process of software design. CS 250: Software Development Lifecycle was created on June 2018. It showed the process of Agile development and the roles that are within it. IT 315: Object Oriented Analysis and Design was created on March 2019. It showed the different designs to help establish and organize the client requirements for an app to aid developers. This included sequence and use case diagrams.
The reason for the inclusion of these artifacts is that each one shows an aspect of the software design. When people think software, they think of the code that is developed but the whole software process is so much more than just the code. It might take the longest to develop the code, but what about the design process, the preparation, the testing, and the feedback of clients. This is all part of the software process. I want to showcase that process through the combination of these artifacts. CS 250 allows me to show my in-depth knowledge and understanding of the Agile process and the different roles involved. Agile process is unique to software design because of the concept of iteration. Understanding the roles also helps in being able to collaborate with the people involved with the process effectively. IT 315 is designing and organizing what the client has tasked the team to do. This showcases my ability to take in information from the clients and organize it in a way to be presented to the team. It also shows my ability to prepare before delving into a code. CS 320 will showcase my ability to test different components of the software. It will also exemplify my ability to code in Java when I fix the code that I tested. These artifacts were improved by taking these different artifacts and combining them to show what a typical software process looks like. From preparing the requirements using a use case diagram to the testing phase of the code and eventually the release of the product.
The expected course outcomes for this enhancement was met. Knowing the process and understanding allows for better collaboration among peers and third parties. It helps understand everyone’s individual role and help make the best decision within the field. The testing aspect of this artifact is crucial for the second outcome that was laid out which was looking for vulnerabilities, mitigating design flaws, privacy and security. The aspect of preparing before coding and making sure documentation is accurate helps avoid flaws or vulnerabilities before they even happen.
Reflecting on the process of enhancing this artifact, there were many things to consider. The whole software process is not simple as what it might seem on a chart. Though I went through a simplified process, I still felt overwhelmed by the whole thing. There are so many steps and I had to take some of those steps multiple times to get a product that a client would be happy to release. I can only imagine if I had to code from scratch. The allotted time for this class would not be enough but I am also one person. The software process is a collaborative effort and that is really an important aspect I was not able to experience. Though I understand the importance and imagine how I would collaborate in real life having firsthand experience would be the best. The other important thing I learned about myself is that I am still struggling to write code. I surely have gotten better at it and understand the concepts involved. When I was fixing the errors, it did take me awhile and a lot of trial and error to get them to function. But I know I should be a lot more confident in my ability to code. Going through my enhancement, my code lacks comments throughout and doing this enhancement let me be more aware of that as a developer.
Enhancement Text
Agile development helps solve many of these problems. The basic method is to work in iterations. Each individual task will go through the whole cycle from planning to developing all the way to testing. This allows for the requirements of a project to be flexible and because of this, communication is a must between the client and the team. For Agile development to be successfully implemented, there are some key features to consider. The first are the different roles involved which are the scrum master, product owner, tester, and developer. The second are phases within the Agile development. For this scenario, a local hospital has hired the company (myself) to create a medical application. Each role will be part of each phase but at certain phases some roles will become more prominent.
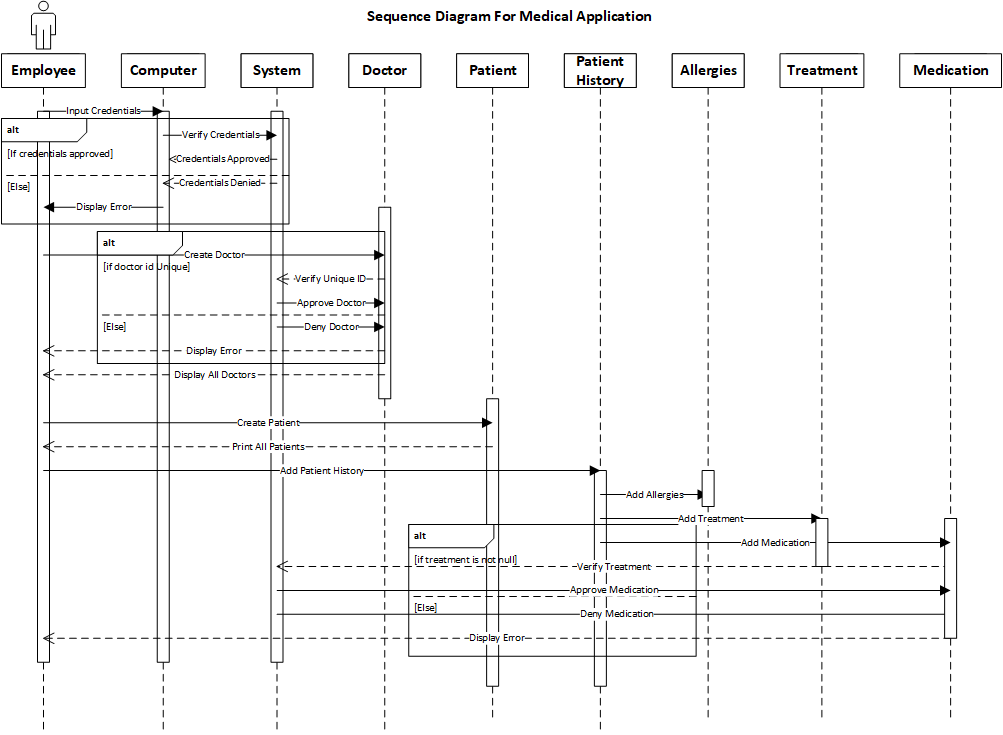
The scrum master is the “coach” of the development team which consist of the tester and developer. It is the scrum master’s job to guide the development team and to facilitate meetings called scrum ceremonies. Scrum ceremonies include sprint planning, daily standups, backlog grooming, and sprint retrospective. All these meetings help guide the team on what tasks to accomplish, their progress, and discuss any problems they are having. Scrum masters are the mediator for collaboration for the development team and the other roles. These meetings can help prepare for coding which leads to the first tools, use case diagrams and sequence diagrams. These tools help the team identify possible classes and the functionality that must be met.
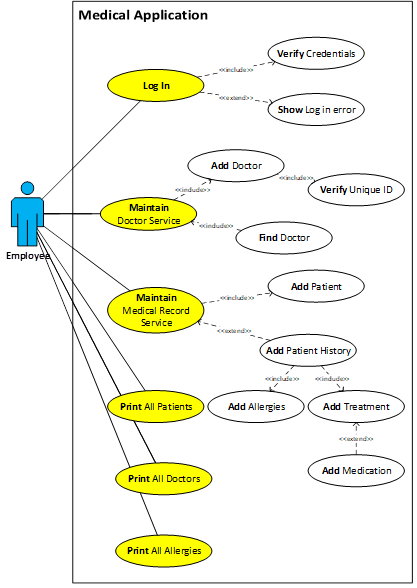
The product owner is the mediator between the customer and the development team and ensures that the team is on track to finish at the deadline. To organize and prioritize the different requirements that the customer asks for, product backlogs and user stories are utilized and given to the development team. As a product owner, communication is key to success. The project relies on how well they communicate to the customer to get the requirements and to update them on the progress and issues of the project. They must also communicate well with the development team. It is the product owner’s job that they receive the requirements for the project and to get updates on the team’s progression. The initial meeting with the customer and presentation on the final product are the main times that a project manager communicates with the customer. A product owner consistently meets with the customer to keep them involved with the project as much as possible.
A tester is someone who lays out the requirements for a task to be considered done and tests the product. A test case is established and given to the developers as a guideline on how to go about the task. The input and expected results are part of the test cases. In Agile development, the definition of done depends on each task. A task does not have to go through the same test or process as other tasks. Each task has its own definition of done. Testing in Agile development is done as often as it can. Each sprint has a testing phase and there are multiple sprints within a project. A good methodology is “fail fast” (Porter, 2006). If you know right away that something does not work, it allows you to fix it at an earlier time and to learn from it, so you do not make the same mistake twice. In the medical application, there are errors in spelling and functionality. When testing it is not just simply looking at the functionality of the code but the structure, security, variables, and documentation. When performing a code review, the code itself was lacking in comments and this was fixed for this enhancement.
The developer creates the actual product based on what the customer requires. A developer knows exactly what it takes to complete each task and how much effort and time it will take. The products are based on the requirements from the user stories that the product owner has created. It is key as a developer to communicate with the rest of the team on the progress of the project and any questions or clarifications on the user stories. There can be multiple people as developers so communication among them is important. This guarantees that everyone is working on different tasks or when fit, can collaborate with each other. Agile development progresses through several iterations.
There are several phases to Agile development. The phases are sprint planning, creation of product backlog and user stories, development of the product, testing, and completion. This is not a step by step approach like Waterfall where one phase follows another and once a phase is done there is no going back. This is more of a framework and can be adjusted accordingly. Typically, a meeting will be held with the customer and product owner to discuss the project and the desired requirements. This will not be the only meeting with the customer and product owner. They will have several meetings throughout the process. The product owner will create user stories and a product backlog. This allows for all the information to be organized. He will present this to the rest of team which include the scrum master, tester, and developer, and together they will plan out a sprint. The scrum master will be leading this meeting. This phase is called sprint planning. A sprint or an iteration usually lasts 1- 4 weeks. In Waterfall development, there is only one time that they go through all the different phases. Agile development breaks it down into smaller tasks. For instance, the project is to create a medical application. Instead of creating the whole application all at once, each sprint will focus on one aspect of the application. The first sprint can work on the login. The second sprint can be about doctor service and so on. Each sprint goes through each phase just like a whole project in Waterfall development. Sprint planning organizes the tasks and prioritizes them. During this step, the developer and tester also gives the product owner a user points which is used to estimate the amount of effort needed for the task. They use a method called planning poker to estimate the amount of effort.
Once sprint planning is finished, it is time to start the development of the product. Every day, the scrum master will hold a daily standup before work starts. This is a short 15-minute meeting with the development team. Each member must answer these questions. The three important questions are what was done yesterday, what is the plan for today, and what obstacles do you foresee happening. A Kanban chart either an online or physical one can be used to visualize and note everyone’s answers. This helps the team collaborate and plan what they are going to do for the day. Another important meeting held during development is the grooming of the product backlog. This is to reevaluate all the tasks from the beginning. As the project progresses, the team will have a better understanding whether an original task is needed or modified. The development team and/or customer might need to add a new requirement. Agile development makes it much easier for changes to be made to a project making development flexible. This is the case because each task is not totally dependent on the task before it. The way the task is created is key because only the bare minimum is developed. Only the components that would satisfy or make the product work will be created which makes it easy to make changes to already developed parts.
As soon as development has finished on a task, the tester will examine it and make sure it has all the requirements for that task to be considered done. He looks at his test cases as a reference which consists of all the requirements for the task to be considered done. Testing is done as frequent as possible unlike Waterfall where it is only done at the end of the project. This allows to see any problems quickly and the team will able to learn from it earlier on in the project. Development and testing are done numerous times throughout a single sprint. Once a sprint is over, there is a sprint review and sprint retrospective. Sprint review is mostly focused on the product. The product owner and/or the customer inspects the product for a final time. This is not the first time the product owner or the customer sees the product, but it will be the final inspection. The sprint retrospective is focused on the development team. This is where the development team and the scrum master analyze the sprint to see what worked well and what did not. It is a time for the team to share experiences to give each other feedback to help avoid problems in future sprints. After everything is done a new sprint starts and the whole process is done again with new tasks. This happens again and again until the project is done, or the deadline passes.
References
Cobb, C. G. (2015-01-26). The Project Manager’s Guide to Mastering Agile: Principles and Practices for an Adaptive Approach, 1st Edition. [MBS Direct]. Retrieved from https://mbsdirect.vitalsource.com/#/books/9781118991770/
Porter, J. (2006, November 14). The Freedom of Fast Iterations: How Netflix Designs a Winning Web Site. Retrieved from https://articles.uie.com/fast_iterations
Code
Main.app
public class App {
private static List<String> mainMenu = Arrays.asList
("", "Main Menu","Please select from the following
options", "1 Print Patient List", "2 Print
Doctor List", "3 Add a Doctor", "4 Add a Patient",
"5 Medical Records","6 Search for Allergies", "0 to Exit");
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Created for testing purposes password is "Open"
Employee employee = new Employee("Mike", "1111");
//Read console input
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
scanner.useDelimiter(System.getProperty("line.separator"));
int passwordAttempts = 3;
String password = null;
boolean loginSuccess = false;
//Login
while (passwordAttempts > 0 && !loginSuccess) {
System.out.println("Login Enter Password");
password = scanner.next();
loginSuccess = employee.getPassword().equals(password);
passwordAttepts--;
}
if (loginSuccess) {
MedicalRecordPrompt medicalRecordPrompt = new
MedicalRecordPrompt();
int input = -1;
System.out.println("Welcome to Mercy Hospital System");
while (input != 0) {
mainMenu.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
input = scanner.nextInt();
switch (input) {
case 1:
//Get all patients
MedicalRecordService.getReference().
getAllPatients().forEach
(System.out::println);
break;
case 2:
//Get all doctors
DoctorService.getReference().
getAllDoctors().
forEach
(System.out::println);
break;
case 3:
//add doctor
addPerson(true, scanner);
break;
case 4:
//add patient
addPerson(false, scanner);
break;
case 5:
//direct to medical prompt
medicalRecordPrompt.mainPrompt(scanner);
break;
case 6:
//get patients with allergies
medicalRecordPrompt.
findAllPatientsWithAllergy
(scanner).
forEach(System.out::println);
break;
case 0:
//exiting system
System.out.println("Good bye!");
break;
default:
break;
}
}
scanner.close();
}else{
System.out.println("Invalid Password after 3 tries");
}
}
//functionality for adding doctor or patient
private static void addPerson(boolean addDoctor, Scanner scanner) {
int input = -1;
String person = addDoctor ? "Doctor" : "Patient";
while (input != 0) {
Pair response = MenuUtil.createTwoItemMenu(scanner,
"Enter Name:", "Enter ID:");
boolean personAdded = false;
if (addDoctor) {
//adding doctor
personAdded = DoctorService.getReference().addDoctor
(response.getOne(),
response.getTwo());
} else {
//adding patient
personAdded = MedicalRescordService.getReference().
addPatient
(response.getOne(), response.getTwo());
}
if (personAdded) {
System.out.println(person + " " + response.getOne()
+ " was succesfully added\n");
} else {
System.out.println(person + " " + response.getOne()
+ " Could not be added\n");
}
System.out.println(
"Would you like to add another " + person
+ "?\n 1 for Yes\n 0
To return to the Main Menu");
input = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
}